pH 스케일은 산성 또는 알칼리성이 어떤지를 측정합니다. 중성 물질 인 순수 또는 증류수의 pH는 7입니다. 그러나 물의 온도를 높이면 pH가 떨어집니다. 그러나이 변화는 pH 테스트 스트립으로는 거의 감지되지 않을 것입니다.
TL, DR (너무 오래, 읽지 않음)
순수한 물의 pH 수준은 온도가 증가함에 따라 떨어지고 온도가 감소함에 따라 상승하지만, 이러한 변화는 너무 작아서 기본적인 pH 테스트 방법으로는 선택할 수 없습니다.
pH 스케일
당신은 단순히 산성 또는 알칼리성 용액의 관점에서 pH 스케일을 생각하는 데 익숙 할 수 있습니다. 7 미만의 pH는 산성을 의미하고 7보다 큰 pH는 알칼리성을 의미한다. 그러나 이것은 또한 용액의 수소 이온 농도의 척도이기도합니다. 수소 이온 농도가 높은 용액은 수소 이온 농도가 낮은 용액보다 낮은 pH를 갖습니다. 하나의 pH의 차이 (즉, pH 5 내지 pH 6)는 수소 이온 농도의 10 배 차이이다.
르 샤텔리의 원리
Le Châtelier의 원리는 화학 평형의 핵심 개념입니다. 이 원칙에 따르면 평형 상태에서 시스템을 나타내는 요인 중 하나를 변경하면 평형 상태가 변화에 대응하도록 이동합니다. 화학 반응의 조건을 변경하는 한 가지 방법은 온도를 변경하는 것입니다. 이것을 물의 온도와 pH 수준에 적용하면 물의 온도를 높이면 평형 상태가 다시 시작되어 온도가 낮아지며 추가 열을 흡수합니다. 이것은 더 많은 수소 이온과 수산화 이온을 만들어내어 물의 pH를 낮 춥니 다. 섭씨 0도에서 섭씨 10도까지 온도가 상승하면 pH가 0.2 감소합니다. 온도를 낮추면 반대가 일어납니다 : pH 수준이 아주 약간 증가합니다.
산도와 산도의 차이
물의 pH가 떨어지더라도 고온에서 물이 더 산성이되는 것은 아닙니다. 수산화 이온보다 높은 수준의 수소 이온이 존재하는 경우에만 용액이 더 산성이 될 수 있습니다. 순수한 물의 경우, 수소 이온과 수산화물 이온의 농도는 결코 변하지 않으므로, 물의 pH 수준이 변경되는지 여부에 관계없이 물은 항상 중성입니다. 실온 (섭씨 25도)에서 순수한 물의 pH는 7입니다. 온도를 섭씨 100 도로 올리면 순수한 물의 pH는 6.14입니다. pH가 7보다 낮더라도 pH는 여전히 중립입니다.
https://ko.science19.com/effects-of-temperature-on-ph-of-water-7185
https://www.westlab.com/blog/2017/11/15/how-does-temperature-affect-ph
How Does Temperature Affect pH? Westlab
Temperature plays a significant role on pH measurements. As the temperature rises, molecular vibrations increase which results in the ability of water to ionise and form more hydrogen ions. As a result, the pH will drop. The dissociation of water into hy
www.westlab.com
Temperature plays a significant role on pH measurements. As the temperature rises, molecular vibrations increase which results in the ability of water to ionise and form more hydrogen ions. As a result, the pH will drop. The dissociation of water into hydrogen and hydroxide ion can be represented as:
H2O (l) ⇌ H+ (aq) + OH− (aq)
Every solution will undergo a change in their pH value through changes in temperature. A difference in pH measurements at different temperatures is NOT an error! The new pH level simply tells about the true pH for that solution at that specific temperature.
The value of Kw (Water ionisation constant) and pH with increasing temperature

It is clearly evident from the table that the pH of water at 0oC is 7.47, but the same water at 100°C will have a pH of 6.14*.
Typical pH values for solutions at different temperatures
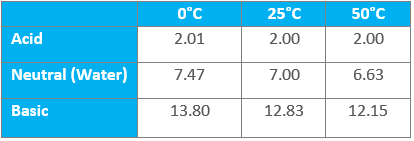
From the table, we can conclude that the effect of temperature is greatest for highly basic solutions.
Common Oversight with pH testing
A common oversight is when you take a sample from a process tank and make the pH measurement in the laboratory. At that time, you are probably not measuring pH at the same temperature as the temperature in the process tank, this means that you will not have the correct pH value for the sample. Thus a pH value without a temperature value is meaningless. This can be simply overcome by testing pH on site and at the source of the sample.
Types of Temperature Compensation
There are two common types of temperature compensation when working with pH measurements.
- Automatic Temperature Compensation (ATC) compensates for the fluctuating milli-volt output from the electrode. ATC is commonly built into today’s pH meters for quick and accurate results.
- Solution Temperature Compensation (STC) (whether this is needed will depend on the pH accuracy required) converts the pH at the measurement temperature to the pH at a reference temperature. The reference temperature is generally 25°C. Only pH values taken at the same temperature or converted using solution temperature compensation can be compared to each other.
Remember that solution temperature effect and electrode temperature effect are different. To get your best results in pH measurement, always remember to calibrate and measure at the same temperature.
Summary
- The pH value of a solution is directly dependent on the temperature.
- A pH value without a temperature value is incoherent.
- Solution temperature compensation (STC) converts measured pH to the pH at 25°C.
- pH values taken at the same temperature or converted using solution temperature compensation can be compared to each other.
- To achieve highest accuracy, calibrate and measure at the same temperature.
*pH decreases with increase in temperature. But this does not mean that water becomes more acidic at higher temperatures. A solution is considered as acidic if there is an excess of hydrogen ions over hydroxide ions. In the case of pure water, there are always the same concentration of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions and hence, the water is still neutral (even if its pH changes). At 100°C, a pH value of 6.14 is the New neutral point on the pH scale at this higher temperature.
번역본!!!
온도가 pH에 어떤 영향을 미칩니까?
- 게시자: westlabblogcanada
- 2017년 11월 15일
- 0 댓글

온도는 pH 측정에서 중요한 역할을 합니다. 온도가 상승함에 따라 분자 진동이 증가하여 물이 이온화되고 더 많은 수소 이온을 형성하는 능력이 생깁니다. 결과적으로 pH가 떨어집니다. 물의 수소 이온과 수산화 이온으로의 해리는 다음과 같이 나타낼 수 있습니다.
H2O(l) ⇌ H+(수성) + OH-(수성)
모든 용액은 온도 변화를 통해 pH 값의 변화를 겪습니다. 다른 온도에서 pH 측정의 차이는 오류가 아닙니다! 새로운 pH 수준은 단순히 특정 온도에서 해당 용액의 실제 pH에 대해 알려줍니다.
온도 증가에 따른 Kw(물 이온화 상수) 및 pH 값

0oC에서 물의 pH가 7.47이지만 100°C에서 동일한 물의 pH는 6.14*임을 표에서 분명히 알 수 있습니다.
다양한 온도에서 용액의 일반적인 pH 값
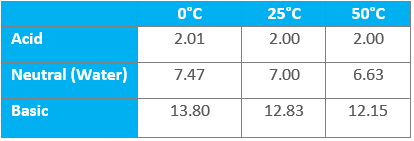
표에서 우리는 온도의 영향이 매우 기본적인 솔루션에서 가장 크다는 결론을 내릴 수 있습니다.
pH 테스트에 대한 일반적인 감독
일반적인 실수는 공정 탱크에서 샘플을 채취하여 실험실에서 pH를 측정하는 것입니다. 그 때, 아마도 공정 탱크의 온도와 동일한 온도에서 pH를 측정하지 않을 것입니다. 이는 샘플에 대한 정확한 pH 값을 갖지 못할 것임을 의미합니다. 따라서 온도 값이 없는 pH 값은 의미가 없습니다. 이는 현장과 샘플 소스에서 pH를 테스트하여 간단히 극복할 수 있습니다.
온도 보상 유형
pH 측정으로 작업할 때 두 가지 일반적인 유형의 온도 보상이 있습니다.
- 자동 온도 보상(ATC)은 전극의 변동하는 밀리볼트 출력을 보상합니다. ATC는 일반적으로 빠르고 정확한 결과를 위해 오늘날의 pH 미터에 내장되어 있습니다.
- 용액 온도 보상(STC)(필요한지 여부는 필요한 pH 정확도에 따라 다름)은 측정 온도의 pH를 기준 온도의 pH로 변환합니다. 기준 온도는 일반적으로 25°C입니다. 동일한 온도에서 측정하거나 용액 온도 보상을 사용하여 변환한 pH 값만 서로 비교할 수 있습니다.
용액 온도 효과와 전극 온도 효과가 다르다는 것을 기억하십시오. pH 측정에서 최상의 결과를 얻으려면 항상 동일한 온도에서 교정하고 측정해야 합니다.
요약
- 용액의 pH 값은 온도에 직접적으로 의존합니다.
- 온도 값이 없는 pH 값은 일관성이 없습니다.
- 용액 온도 보상(STC)은 측정된 pH를 25°C에서 pH로 변환합니다.
- 동일한 온도에서 측정하거나 용액 온도 보상을 사용하여 변환한 pH 값을 서로 비교할 수 있습니다.
- 최고의 정확도를 얻으려면 동일한 온도에서 교정 및 측정하십시오.
*pH는 온도가 증가함에 따라 감소합니다. 그러나 이것이 물이 더 높은 온도에서 더 산성이 된다는 것을 의미하지는 않습니다. 수산화 이온보다 수소 이온이 과도하게 많으면 용액이 산성으로 간주됩니다. 순수한 물의 경우 수소 이온과 수산화 이온의 농도는 항상 같으므로 물은 여전히 중성입니다(pH가 변하더라도). 100°C에서 6.14의 pH 값은 이 더 높은 온도에서 pH 척도의 새로운 중성점입니다.
내가내린결론 온도와pH관계:
온도가 올라가면 pH내려가고 기준은 25도로 해야한다
'업무관련' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 의료기기 1등급 통합 정보 등록하기 (0) | 2022.05.26 |
|---|---|
| UDI 1등급 의료기기 UDI 바코드 생성방법 (0) | 2022.05.25 |
| KCL 시험진행현황 조회 사이트 (0) | 2022.03.16 |
| 2022 의약품안전관리 정책설명회 자료 (0) | 2022.03.16 |
| ICH 가이드라인 번역본 (0) | 2022.03.15 |


